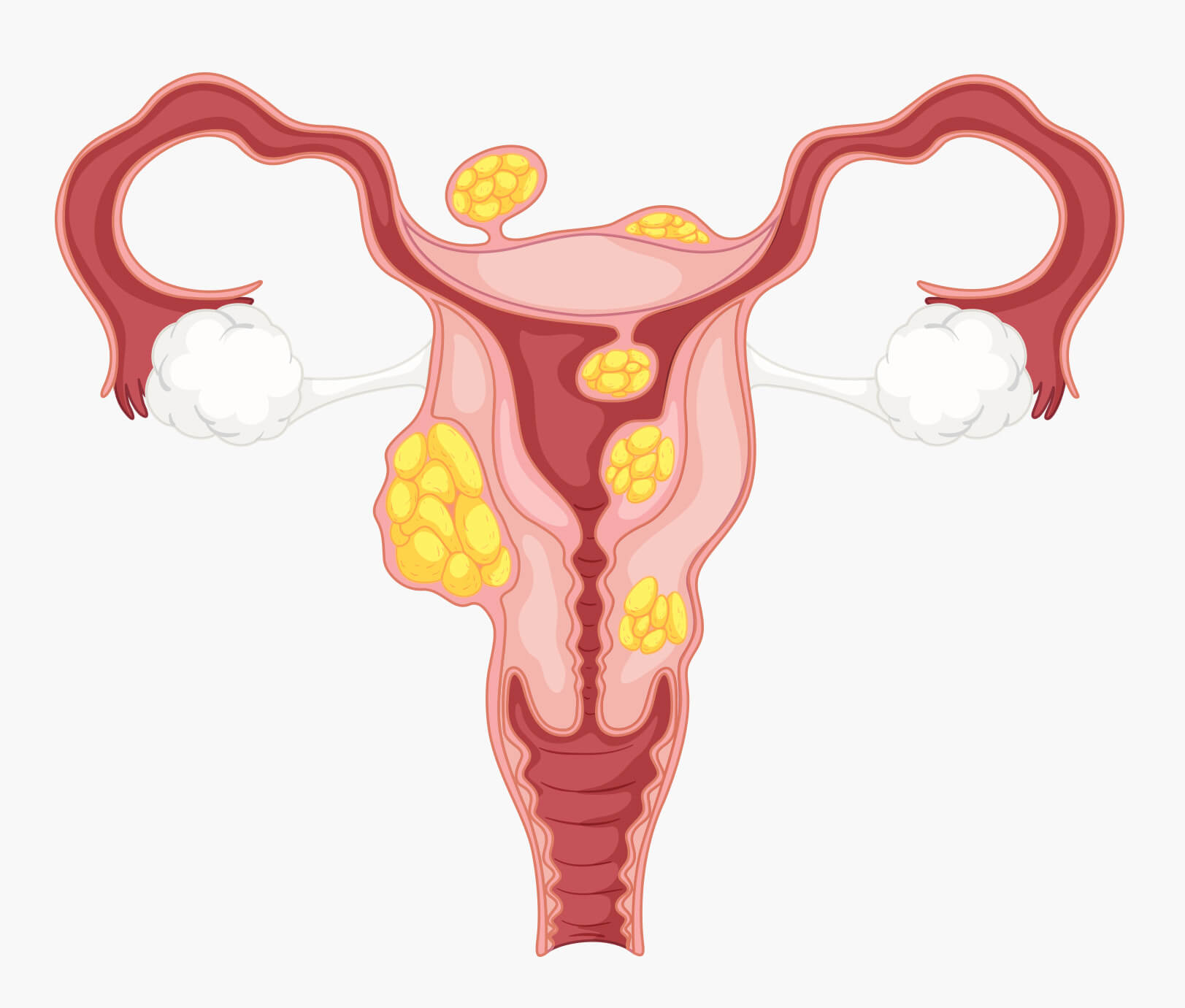
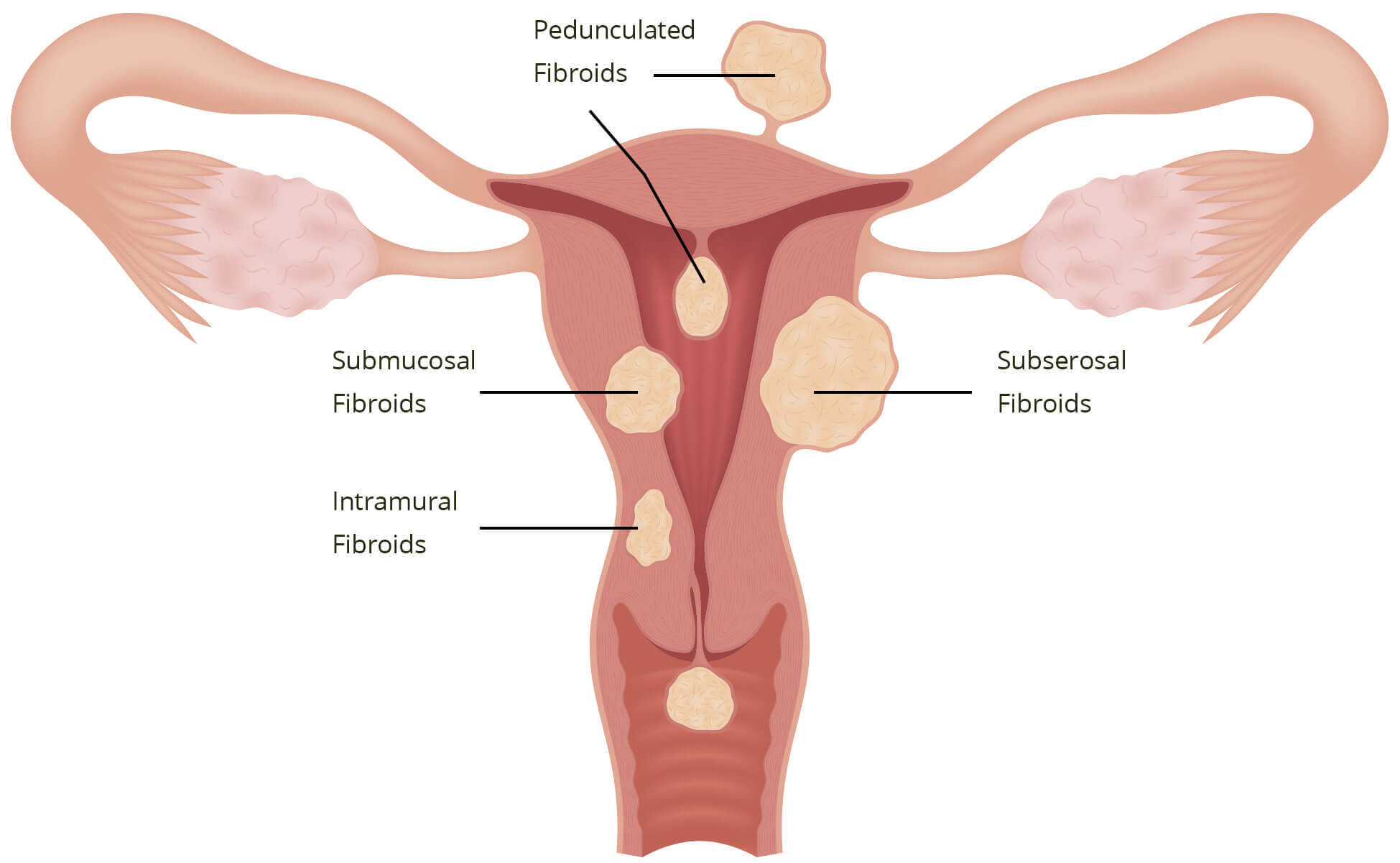
Uterine fibroids are abnormal growths on the uterus.
About 30% of women above the age of 35 will have uterine fibroids. Fortunately, the risk of the fibroids being cancerous remains low and, in most cases, they do not cause any symptoms nor affect daily activities. Uterine fibroids vary in size and numbers, with some only growing to the size of an apple seed.